|
Greek city of Katane in Sicily
Bronze Dekonkion 20mm (4.30 grams) Struck after 212 B.C.
Reference: Sear 1072; B.M.C. 2.62
Jugate busts of Zeus Serapis and Isis right; ear of corn behind, X before.
KATANAIΩN, Apollo standing facing, holding
laurel-branch and bow, and resting left elbow
on column; quiver and omphalos at
feet.
Following the capture by Hieron of Syracuse, in 476 B.C., the
name of this city was changed to Aitna; but on the expulsion of the the new
colonists, fifteen years later, the place reverted to its original name of
Katane. It was captured in 404 B.C. by Dionysios of Syracuse who sold the
population into slavery. Katane submitted to Rome during the First Punic War.
You are bidding on the exact
item pictured, provided with a Certificate of Authenticity and Lifetime
Guarantee of Authenticity. Isis
or in original more likely Aset was a goddess in
Ancient Egyptian
religious beliefs, whose
worship spread throughout the
Greco-Roman world
. She was worshiped as the
ideal mother and wife as well as the matron of nature and magic. She was the
friend of slaves, sinners, artisans, the downtrodden, as well as listening to
the prayers of the wealthy, maidens, aristocrats and rulers. Isis is the Goddess
of
motherhood
,
magic
and
fertility
.
The goddess Isis (the mother of
Horus
) was the first daughter of
Geb,
god of the Earth, and
Nut
, the goddess of the Overarching Sky, and
was born on the fourth
intercalary day
. At some time Isis and
Hathor
had the same headdress. In later myths
about Isis, she had a brother,
Osiris
, who became her husband, and she then
was said to have conceived
Horus
. Isis was instrumental in the
resurrection of Osiris when he was murdered by
Set
. Her magical skills restored his body to
life after she gathered the body parts that had been strewn about the earth by
Set. This myth became very important in later Egyptian religious beliefs.
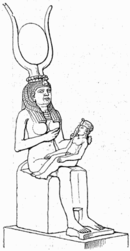
Isis nursing Horus, wearing the headdress of Hathor
Isis is also known as the goddess of
simplicity
, protector of the dead and goddess
of children from whom all beginnings arose. In later myths, the Ancient
Egyptians
believed that the
Nile River
flooded every year because of her
tears of sorrow for her dead husband, Osiris. This occurrence of his death and
rebirth was relived each year through rituals. The worship of Isis eventually
spread throughout the Greco-Roman world, continuing until the suppression of
paganism
in the Christian era.
Serapis (Latin spelling, or Sarapis in Greek) was a
syncretic
Hellenistic
-Egyptian
god in
Antiquity
. His most renowned temple was the
Serapeum
 of Alexandria.
Under
Ptolemy Soter
, efforts were made to integrate Egyptian religion with that of
their Hellenic rulers. Ptolemy's policy was to find a deity that should win the
reverence alike of both groups, despite the curses of the Egyptian priests
against the gods of the previous foreign rulers (i.e
Set
who was lauded by the
Hyksos
).
Alexander the Great
had attempted to use
Amun for this
purpose, but he was more prominent in
Upper
Egypt
, and not as popular with those in
Lower
Egypt
, where the Greeks had stronger influence. The Greeks had little
respect for animal-headed figures, and so a Greek-style
anthromorphic
statue was chosen as the
idol
,
and proclaimed as the equivalent of the highly popular
Apis
.
It was named Aser-hapi (i.e. Osiris-Apis), which became Serapis,
and was said to be Osiris
in full, rather than just his
Ka
(life force).
of Alexandria.
Under
Ptolemy Soter
, efforts were made to integrate Egyptian religion with that of
their Hellenic rulers. Ptolemy's policy was to find a deity that should win the
reverence alike of both groups, despite the curses of the Egyptian priests
against the gods of the previous foreign rulers (i.e
Set
who was lauded by the
Hyksos
).
Alexander the Great
had attempted to use
Amun for this
purpose, but he was more prominent in
Upper
Egypt
, and not as popular with those in
Lower
Egypt
, where the Greeks had stronger influence. The Greeks had little
respect for animal-headed figures, and so a Greek-style
anthromorphic
statue was chosen as the
idol
,
and proclaimed as the equivalent of the highly popular
Apis
.
It was named Aser-hapi (i.e. Osiris-Apis), which became Serapis,
and was said to be Osiris
in full, rather than just his
Ka
(life force).
In the
ancient Greek
religion
, Zeus
zews
zooss
;
Ancient Greek
: Ζεύς;
Modern
Greek
: Δίας, Dias) was the "Father of Gods and men" (πατὴρ
ἀνδρῶν τε θεῶν τε) who ruled the Olympians of
Mount
Olympus
as a father ruled the family. He was the
god of sky
and
thunder
in
Greek mythology
. His
Roman
counterpart is
Jupiter
and
Etruscan
counterpart is
Tinia
.![The Jupiter de Smyrne, discovered in Smyrna in 1680[1]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/c/c8/Jupiter_Smyrna_Louvre_Ma13.jpg/200px-Jupiter_Smyrna_Louvre_Ma13.jpg)
Zeus was the child of
Cronus
and
Rhea
, and the youngest of his siblings. In most
traditions he was married to
Hera, although, at the oracle of
Dodona
, his consort was
Dione
: according to the
Iliad
, he is the father of
Aphrodite
by Dione.[2]
He is known for his erotic escapades. These resulted in many godly and heroic
offspring, including
Athena
,
Apollo
and
Artemis
,
Hermes
,
Persephone
(by
Demeter
),
Dionysus
,
Perseus
,
Heracles
,
Helen of Troy
,
Minos
, and the
Muses (by
Mnemosyne
); by Hera, he is usually said to have
fathered
Ares
,
Hebe
and
a title="Hephaestus" href="https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hephaestus" style="text-decoration: none">
Hephaestus.[5]
As
Walter Burkert
points out in his book, Greek
Religion, "Even the gods who are not his natural children address him as
Father, and all the gods rise in his presence."[6]
For the Greeks, he was the
King of the Gods
, who oversaw the universe. As
Pausanias
observed, "That Zeus is king in
heaven is a saying common to all men".[7]
In Hesiod's
Theogony
Zeus assigns the various gods
their roles. In the
Homeric Hymns
he is referred to as the
chieftain of the gods.
His symbols are the
thunderbolt
,
eagle
,
bull
, and
oak.
In addition to his Indo-European inheritance, the classical "cloud-gatherer"
also derives certain iconographic traits from the cultures of the
Ancient Near East
, such as the
scepter
. Zeus is frequently depicted by Greek
artists in one of two poses: standing, striding forward, with a thunderbolt
leveled in his raised right hand, or seated in majesty.
Etymology

The Chariot of Zeus, from an 1879 Stories from the Greek
Tragedians by Alfred Church
In Greek, the god's name is Ζεύς
Zeús
/zdeús/ or
/dzeús/ (Modern Greek
/ˈzefs/) in the
nominative case
and
Διός Diós in the
genitive case
. The earliest forms of the name
are the
Mycenaean Greek
di-we and di-wo,
written in
Linear b
syllabic script.[8]
With the apparent interchangeability of "z" and "d", Zeus can also be
Deus.
Zeus, poetically referred to by the
vocative
Zeu pater ("O, father Zeus"),
is a continuation of *Di̯ēus,
the
Proto-Indo-European
god of the daytime sky,
also called *Dyeus
ph2tēr ("Sky Father").[9]
The god is known under this name in
Sanskrit
(compare
Dyaus/Dyaus Pita
),
Latin
(compare
Jupiter
, from Iuppiter, deriving
from the
Proto-Indo-European
vocative *dyeu-ph2tēr[10]),
deriving from the basic form *dyeu- ("to shine", and in its many
derivatives, "sky, heaven, god").[9]
And in
Germanic mythology
(compare *Tīwaz
>
Old High German language
Ziu,
Old Norse
Týr
), together with Latin deus,
dīvus and Dis (a variation of dīves[11]),
from the related noun *deiwos.[11]
To the Greeks and Romans, the god of the sky was also the supreme god. Zeus is
the only deity in the Olympic
pantheon
whose name has such a transparent
Indo-European etymology.
 In
Greek
and
Roman mythology
, Apollo
,
is one of the most important and diverse of the
Olympian deities
. The ideal of the
kouros
(a
beardless youth), Apollo has been variously recognized as a god of light and the
sun; truth and prophecy;
archery
;
medicine and healing; music, poetry, and the arts; and more. Apollo is the son
of Zeus
and
Leto, and has a
twin
sister, the chaste huntress
Artemis
.
Apollo is known in Greek-influenced
Etruscan mythology
as Apulu. Apollo was worshiped in both
ancient Greek
and
Roman religion
, as well as in the modern
Greco
-Roman
Neopaganism
.
In
Greek
and
Roman mythology
, Apollo
,
is one of the most important and diverse of the
Olympian deities
. The ideal of the
kouros
(a
beardless youth), Apollo has been variously recognized as a god of light and the
sun; truth and prophecy;
archery
;
medicine and healing; music, poetry, and the arts; and more. Apollo is the son
of Zeus
and
Leto, and has a
twin
sister, the chaste huntress
Artemis
.
Apollo is known in Greek-influenced
Etruscan mythology
as Apulu. Apollo was worshiped in both
ancient Greek
and
Roman religion
, as well as in the modern
Greco
-Roman
Neopaganism
.
As the patron of Delphi
(Pythian Apollo), Apollo was an
oracular
god — the prophetic deity of the
Delphic Oracle
.
Medicine and healing were associated with Apollo, whether through the god
himself or mediated through his son
Asclepius
,
yet Apollo was also seen as a god who could bring ill-health and deadly
plague
as well as one who had the ability to cure. Amongst the god's
custodial charges, Apollo became associated with dominion over
colonists
, and as the patron defender of herds and flocks. As the leader of
the Muses
(Apollon
Musagetes) and director of their choir, Apollo functioned as the patron god
of music and poetry
.
Hermes
created
the lyre
for him,
and the instrument became a common
attribute
of Apollo. Hymns sung to Apollo were called
paeans
.
In Hellenistic times, especially during the third century BCE, as Apollo
Helios he became identified among Greeks with
Helios
,
god of
the sun
, and his sister Artemis similarly equated with
Selene
,
goddess
of the moon
.
In Latin texts, on the other hand, Joseph Fontenrose declared himself unable to
find any conflation of Apollo with
Sol
among the
Augustan poets
of the first century, not even in the conjurations of
Aeneas
and
Latinus
in
Aeneid
XII
(161–215).
Apollo and Helios/Sol remained separate beings in literary and mythological
texts until the third century CE.
Foundation
All ancient authors agree in representing Catania as a
Greek colony
named
Κατάνη ('Katánē—see also
List of traditional Greek place names
) of
Chalcidic
origin, but founded immediately from
the neighboring city of
Naxos
, under the guidance of a leader named
Euarchos (Euarchus).
The exact date of its foundation is not recorded, but it appears from
Thucydides
to have followed shortly after that
of Leontini (modern
Lentini
), which he places in the fifth year
after
Syracuse
, or
730 BC
.
Greek
Sicily
The only event of its early history that has been transmitted to us is the
legislation of
Charondas
, and even of this the date is wholly
uncertain.
But from the fact that his legislation was extended to the other Chalcidic
cities, not only of Sicily, but of
Magna Graecia
also, as well as to his own
country, it is evident that Catania continued in intimate relations with these
kindred cities.
It seems to have retained its independence till the time of
Hieron of Syracuse
, but that despot, in
476 BC
, expelled all the original inhabitants,
whom he established at Leontini, while he repeopled the city with a new body of
colonists, amounting, it is said, to not less than 10,000 in number, and
consisting partly of
Syracusans
, partly of
Peloponnesians
.
He at the same time changed the city's name to
Αἴτνη (Aítnē, Aetna or Ætna,
after the nearby
Mount Etna
, an active
volcano
), and caused himself to be proclaimed
the
Oekist
or founder of the new city. As such he
was celebrated by Pindar
, and after his death obtained heroic
honors from the citizens of his new colony.
But this state of things was of brief duration, and a few years after the
death of Hieron and the expulsion of
Thrasybulus
, the Syracusans combined with
Ducetius
, king of the
Siculi
, to expel the newly settled inhabitants
of Catania, who were compelled to retire to the fortress of
Inessa
(to which they gave the name of Aetna),
while the old Chalcidic citizens were reinstated in the possession of Catania,
461 BC
.
The period that followed the settlement of affairs at this epoch appears to
have been one of great prosperity for Catania, as well as for the Sicilian
cities in general: however, no details of its history are known till the great
Athenian
expedition to Sicily
(part of the larger
Peloponnesian War
).
On that occasion the Catanaeans, notwithstanding their Chalcidic connections,
at first refused to receive the Athenians into their city: but the latter having
effected an entrance, they found themselves compelled to espouse the alliance of
the invaders, and Catania became in consequence the headquarters of the Athenian
armament throughout the first year of the expedition, and the base of their
subsequent operations against Syracuse.
There is no information as to the fate of Catania after the close of this
expedition: it is next mentioned in
403 BC
, when it fell into the power of
Dionysius I of Syracuse
, who sold the
inhabitants as slaves, and gave up the city to plunder; after which he
established there a body of
Campanian
mercenaries.
These, however, quit it again in
396 BC
, and retired to
Aetna
, on the approach of the great
Carthaginian
armament under
Himilco
and
Mago
. The great sea-fight in which the latter
defeated
Leptines
, the brother of Dionysius, was fought
immediately off Catania, and the city apparently[ wordsweasel]
fell, in consequence, into the hands of the Carthaginians.
Callippus
, the assassin of Dion of Syracuse,
when he was expelled from Syracuse, for a time held possession of Catania (Plut.
Dion. 58); and when
Timoleon
landed in Sicily Catania was subject
to a despot named
Mamercus
, who at first joined the
Corinthian
leader but afterwards abandoned his
alliance for that of the Carthaginians, and was in consequence attacked and
expelled by Timoleon.
Catania was now restored to liberty, and appears to have continued to retain
its independence; during the wars of
Agathocles
with the Carthaginians, it sided at
one time with the former, at others with the latter; and when
Pyrrhus
landed in Sicily, Catania was the first
to open its gates to him, and received him with the greatest magnificence.
Catania was the birth-place of the philosopher and legislator Charondas; it
was also the place of residence of the poet
Stesichorus
, who died there, and was buried in
a magnificent sepulchre outside one of the gates, which derived from thence the
name of Porta Stesichoreia. (Suda,
under Στησίχορος.)
Xenophanes
, the philosopher of
Elea
, also spent the latter years of his life
there, so that it was evidently, at an early period, a place of cultivation and
refinement.
The first introduction of dancing to accompany the flute, was also ascribed
to
Andron
, a citizen of Catania
In ancient times Catania was associated with the legend of
Amphinomus and Anapias
, who, on occasion of a
great eruption of Etna, abandoned all their property, and carried off their aged
parents on their shoulders, the stream of lava itself was said to have parted,
and flowed aside so as not to harm them. Statues were erected to their honor,
and the place of their burial was known as the Campus Piorum; the
Catanaeans even introduced the figures of the youths on their coins, and the
legend became a favorite subject of allusion and declamation among the
Latin poets
, of whom the younger
Lucilius
and
Claudian
have dwelt upon it at considerable
length.
The occurrence is referred by
Hyginus
to the first eruption of Etna that took
place after the settlement of Catania.
Roman
rule
In the
First Punic War
, Catania was one of the first
among the cities of Sicily, which made their submission to the
Roman Republic
, after the first successes of
their arms in 263 BC. The expression of
Pliny
(vii. 60) who represents it as having
been taken by
Valerius Messalla
, is certainly a mistake.
It appears to have continued afterwards steadily to maintain its friendly
relations with Rome, and though it did not enjoy the advantages of a confederate
city (foederata civitas), like its neighbors Tauromenium (modern
Taormina
) and Messana (modern
Messina
), it rose to a position of great
prosperity under the Roman rule.
Cicero
repeatedly mentions it as, in his time,
a wealthy and flourishing city; it retained its ancient municipal institutions,
its
chief magistrate
bearing the title of
Proagorus; and appears to have been one of the principal ports of Sicily for
the export of corn.
It subsequently suffered severely from the ravages of
Sextus Pompeius
, and was in consequence one of
the cities to which a
colony
was sent by
Augustus
; a measure that appears to have in a
great degree restored its prosperity, so that in
Strabo
's time it was one of the few cities in
the island that was in a flourishing condition.
It retained its colonial rank, as well as its prosperity, throughout the
period of the
Roman Empire
; so that in the 4th century
Ausonius
in his
Ordo Nobilium Urbium
, notices Catania and
Syracuse alone among the cities of Sicily.
One of the most serious
eruptions
of
Mount Etna
happened in
121 BC
, when great part of Catania was
overwhelmed by streams of lava, and the hot ashes fell in such quantities in the
city itself, as to break in the roofs of the houses.
Catania was in consequence exempted, for 10 years, from its usual
contributions to the Roman state The greater part of the broad tract of plain to
the southwest of Catania (now called the Piana di Catania, a district of
great fertility), appears to have belonged, in
ancient times
, to Leontini or Centuripa (modern
Centuripe
), but that portion of it between
Catana itself and the mouth of the Symaethus, was annexed to the territory of
the latter city, and must have furnished abundant supplies of grain.
The port of Catania also, which was in great part filled up by the eruption
of
1669 AD
, appears to have been in ancient times
much frequented, and was the chief place of export for the corn of the rich
neighboring plains. The little river Amenanus, or Amenas, which flowed through
the city, was a very small stream, and could never have been navigable.
|



 of Alexandria.
Under
Ptolemy Soter
, efforts were made to integrate Egyptian religion with that of
their Hellenic rulers. Ptolemy's policy was to find a deity that should win the
reverence alike of both groups, despite the curses of the Egyptian priests
against the gods of the previous foreign rulers (i.e
Set
who was lauded by the
Hyksos
).
Alexander the Great
had attempted to use
Amun for this
purpose, but he was more prominent in
Upper
Egypt
, and not as popular with those in
Lower
Egypt
, where the Greeks had stronger influence. The Greeks had little
respect for animal-headed figures, and so a Greek-style
anthromorphic
statue was chosen as the
idol
,
and proclaimed as the equivalent of the highly popular
Apis
.
It was named Aser-hapi (i.e. Osiris-Apis), which became Serapis,
and was said to be Osiris
in full, rather than just his
Ka
(life force).
of Alexandria.
Under
Ptolemy Soter
, efforts were made to integrate Egyptian religion with that of
their Hellenic rulers. Ptolemy's policy was to find a deity that should win the
reverence alike of both groups, despite the curses of the Egyptian priests
against the gods of the previous foreign rulers (i.e
Set
who was lauded by the
Hyksos
).
Alexander the Great
had attempted to use
Amun for this
purpose, but he was more prominent in
Upper
Egypt
, and not as popular with those in
Lower
Egypt
, where the Greeks had stronger influence. The Greeks had little
respect for animal-headed figures, and so a Greek-style
anthromorphic
statue was chosen as the
idol
,
and proclaimed as the equivalent of the highly popular
Apis
.
It was named Aser-hapi (i.e. Osiris-Apis), which became Serapis,
and was said to be Osiris
in full, rather than just his
Ka
(life force).![The Jupiter de Smyrne, discovered in Smyrna in 1680[1]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/c/c8/Jupiter_Smyrna_Louvre_Ma13.jpg/200px-Jupiter_Smyrna_Louvre_Ma13.jpg)

 In
Greek
and
Roman mythology
, Apollo
,
is one of the most important and diverse of the
Olympian deities
. The ideal of the
kouros
(a
beardless youth), Apollo has been variously recognized as a god of light and the
sun; truth and prophecy;
archery
;
medicine and healing; music, poetry, and the arts; and more. Apollo is the son
of Zeus
and
Leto, and has a
twin
sister, the chaste huntress
Artemis
.
Apollo is known in Greek-influenced
Etruscan mythology
as Apulu. Apollo was worshiped in both
ancient Greek
and
Roman religion
, as well as in the modern
Greco
-Roman
Neopaganism
.
In
Greek
and
Roman mythology
, Apollo
,
is one of the most important and diverse of the
Olympian deities
. The ideal of the
kouros
(a
beardless youth), Apollo has been variously recognized as a god of light and the
sun; truth and prophecy;
archery
;
medicine and healing; music, poetry, and the arts; and more. Apollo is the son
of Zeus
and
Leto, and has a
twin
sister, the chaste huntress
Artemis
.
Apollo is known in Greek-influenced
Etruscan mythology
as Apulu. Apollo was worshiped in both
ancient Greek
and
Roman religion
, as well as in the modern
Greco
-Roman
Neopaganism
.