|
Byzantine -
Manuel I
, Comnenus - Byzantine Emperor: 8
April 1143 - 24 September 1180 A.D.
Bronze Half Tetarteron 14mm (1.65 grams) Struck at Uncertain Greek Mint
circa 1143-1180 A.D.
Reference: Sear 1979
Monogram 58

No legend. Bust of Manuel facing, beardless, wearing crown and loros,
and
holding labarum and globe cross.
Royal/Imperial symbols of power
Ruling dynasties often exploit pomp and ceremony with the use of
regalia
:
crowns
,
robes,
orb (globe) and sceptres
, some of which are
reflections of formerly practical objects. The use of language mechanisms also
support this differentiation with subjects talking of "the crown" and/or of "the
throne
" rather than referring directly to
personal names and items.
You are bidding on the exact
item pictured, provided with a Certificate of Authenticity and Lifetime
Guarantee of Authenticity.

Labarum of Constantine I, displaying the "Chi-Rho" symbol above.
The labarum was a
vexillum
(military standard) that displayed
the "Chi-Rho"
symbol
☧
, formed from the first two
Greek letters
of the word "Christ"
—
Chi
and
Rho
. It was first used by the
Roman emperor
Constantine I
. Since the vexillum consisted of
a flag suspended from the crossbar of a cross, it was ideally suited to
symbolize the
crucifixion
of
Christ
.
Later usage has sometimes regarded the terms "labarum" and "Chi-Rho" as
synonyms. Ancient sources, however, draw an unambiguous distinction between the
two.
Etymology
Beyond its derivation from Latin labarum, the etymology of the word is
unclear. Some derive it from Latin /labāre/ 'to totter, to waver' (in the sense
of the "waving" of a flag in the breeze) or laureum [vexillum] ("laurel
standard"). According to the
Real Academia Española
, the related
lábaro
is also derived from Latin labărum
but offers no further derivation from within Latin, as does the Oxford English
Dictionary.[5]
An origin as a loan into Latin from a Celtic language or
Basque
has also been postulated. There is a
traditional Basque symbol called the
lauburu
; though the name is only attested from
the 19th century onwards the motif occurs in engravings dating as early as the
2nd century AD.
Vision of Constantine

A coin of Constantine (c.337) showing a depiction of his labarum
spearing a serpent.
On the evening of October 27, 312, with his army preparing for the
Battle of the Milvian Bridge
, the emperor
Constantine I
claimed to have had a vision
which led him to believe he was fighting under the protection of the
Christian God
.
Lactantius
states that, in the night before the
battle, Constantine was commanded in a dream to "delineate the heavenly sign on
the shields of his soldiers". He obeyed and marked the shields with a sign
"denoting Christ". Lactantius describes that sign as a "staurogram", or a
Latin cross
with its upper end rounded in a
P-like fashion, rather than the better known
Chi-Rho
sign described by
Eusebius of Caesarea
. Thus, it had both the
form of a cross and the monogram of Christ's name from the formed letters "X"
and "P", the first letters of Christ's name in Greek.
From Eusebius, two accounts of a battle survive. The first, shorter one in
the
Ecclesiastical History
leaves no doubt that
God helped Constantine but doesn't mention any vision. In his later Life of
Constantine, Eusebius gives a detailed account of a vision and stresses that
he had heard the story from the emperor himself. According to this version,
Constantine with his army was marching somewhere (Eusebius doesn't specify the
actual location of the event, but it clearly isn't in the camp at Rome) when he
looked up to the sun and saw a cross of light above it, and with it the Greek
words
Ἐν Τούτῳ Νίκα
. The traditionally employed
Latin translation of the Greek is
in hoc signo vinces
— literally "In this
sign, you will conquer." However, a direct translation from the original Greek
text of Eusebius into English gives the phrase "By this, conquer!"
At first he was unsure of the meaning of the apparition, but the following
night he had a dream in which Christ explained to him that he should use the
sign against his enemies. Eusebius then continues to describe the labarum, the
military standard used by Constantine in his later wars against
Licinius
, showing the Chi-Rho sign.
Those two accounts can hardly be reconciled with each other, though they have
been merged in popular notion into Constantine seeing the Chi-Rho sign on the
evening before the battle. Both authors agree that the sign was not readily
understandable as denoting Christ, which corresponds with the fact that there is
no certain evidence of the use of the letters chi and rho as a Christian sign
before Constantine. Its first appearance is on a Constantinian silver coin from
c. 317, which proves that Constantine did use the sign at that time, though not
very prominently. He made extensive use of the Chi-Rho and the labarum only
later in the conflict with Licinius.
The vision has been interpreted in a solar context (e.g. as a
solar halo
phenomenon), which would have been
reshaped to fit with the Christian beliefs of the later Constantine.
An alternate explanation of the intersecting celestial symbol has been
advanced by George Latura, which claims that Plato's visible god in Timaeus
is in fact the intersection of the Milky Way and the Zodiacal Light, a rare
apparition important to pagan beliefs that Christian bishops reinvented as a
Christian symbol.
Eusebius' description of the labarum
"A Description of the Standard of the Cross, which the Romans now call the
Labarum." "Now it was made in the following manner. A long spear, overlaid with
gold, formed the figure of the cross by means of a transverse bar laid over it.
On the top of the whole was fixed a wreath of gold and precious stones; and
within this, the symbol of the Saviour’s name, two letters indicating the name
of Christ by means of its initial characters, the letter P being intersected by
X in its centre: and these letters the emperor was in the habit of wearing on
his helmet at a later period. From the cross-bar of the spear was suspended a
cloth, a royal piece, covered with a profuse embroidery of most brilliant
precious stones; and which, being also richly interlaced with gold, presented an
indescribable degree of beauty to the beholder. This banner was of a square
form, and the upright staff, whose lower section was of great length, of the
pious emperor and his children on its upper part, beneath the trophy of the
cross, and immediately above the embroidered banner."
"The emperor constantly made use of this sign of salvation as a safeguard
against every adverse and hostile power, and commanded that others similar to it
should be carried at the head of all his armies."
Iconographic career under Constantine

Coin of
Vetranio
, a soldier is holding two
labara. Interestingly they differ from the labarum of Constantine in
having the Chi-Rho depicted on the cloth rather than above it, and
in having their staves decorated with
phalerae
as were earlier Roman
military unit standards.

The emperor
Honorius
holding a variant of the
labarum - the Latin phrase on the cloth means "In the name of Christ
[rendered by the Greek letters XPI] be ever victorious."
Among a number of standards depicted on the
Arch of Constantine
, which was erected, largely
with fragments from older monuments, just three years after the battle, the
labarum does not appear. A grand opportunity for just the kind of political
propaganda that the Arch otherwise was expressly built to present was missed.
That is if Eusebius' oath-confirmed account of Constantine's sudden,
vision-induced, conversion can be trusted. Many historians have argued that in
the early years after the battle the emperor had not yet decided to give clear
public support to Christianity, whether from a lack of personal faith or because
of fear of religious friction. The arch's inscription does say that the Emperor
had saved the
res publica
INSTINCTV DIVINITATIS
MENTIS MAGNITVDINE ("by greatness of mind and by instinct [or impulse]
of divinity"). As with his predecessors, sun symbolism – interpreted as
representing
Sol Invictus
(the Unconquered Sun) or
Helios
,
Apollo
or
Mithras
– is inscribed on his coinage, but in
325 and thereafter the coinage ceases to be explicitly pagan, and Sol Invictus
disappears. In his
Historia Ecclesiae
Eusebius further reports
that, after his victorious entry into Rome, Constantine had a statue of himself
erected, "holding the sign of the Savior [the cross] in his right hand." There
are no other reports to confirm such a monument.
Whether Constantine was the first
Christian
emperor supporting a peaceful
transition to Christianity during his rule, or an undecided pagan believer until
middle age, strongly influenced in his political-religious decisions by his
Christian mother
St. Helena
, is still in dispute among
historians.
As for the labarum itself, there is little evidence for its use before 317.In
the course of Constantine's second war against Licinius in 324, the latter
developed a superstitious dread of Constantine's standard. During the attack of
Constantine's troops at the
Battle of Adrianople
the guard of the labarum
standard were directed to move it to any part of the field where his soldiers
seemed to be faltering. The appearance of this talismanic object appeared to
embolden Constantine's troops and dismay those of Licinius.At the final battle
of the war, the
Battle of Chrysopolis
, Licinius, though
prominently displaying the images of Rome's pagan pantheon on his own battle
line, forbade his troops from actively attacking the labarum, or even looking at
it directly.[16]
Constantine felt that both Licinius and
Arius
were agents of Satan, and associated them
with the serpent described in the
Book of Revelation
(12:9).
Constantine represented Licinius as a snake on his coins.
Eusebius stated that in addition to the singular labarum of Constantine,
other similar standards (labara) were issued to the Roman army. This is
confirmed by the two labara depicted being held by a soldier on a coin of
Vetranio
(illustrated) dating from 350.
Later usage

Modern ecclesiastical labara (Southern Germany).

The emperor
Constantine Monomachos
(centre
panel of a Byzantine enamelled crown) holding a miniature labarum
The Chi Rho is one of the earliest
christograms
used by Christians. It is formed by superimposing the
first two letters in the Greek spelling of the word
Christ
(
Greek
: "Χριστός" ), chi = ch and rho = r, in such a way to produce
the monogram
☧. The Chi-Rho symbol was also used by pagan Greek scribes to
mark, in the margin, a particularly valuable or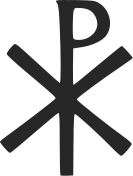 relevant passage; the
combined
letters Chi and Rho standing for chrēston, meaning "good." Although not technically a cross, the Chi Rho invokes the crucifixion
of Jesus as well as symbolizing his status as the Christ. There is early
evidence of the Chi Rho symbol on Christian Rings of the third century. relevant passage; the
combined
letters Chi and Rho standing for chrēston, meaning "good." Although not technically a cross, the Chi Rho invokes the crucifixion
of Jesus as well as symbolizing his status as the Christ. There is early
evidence of the Chi Rho symbol on Christian Rings of the third century.
The labarum (Greek:
λάβαρον) was a
vexillum
(military standard) that displayed the "Chi-Rho"
symbol, formed from the first two
Greek letters
of the word "Christ"
(Greek:
ΧΡΙΣΤΟΣ, or Χριστός) — Chi (χ)
and Rho (ρ).
It was first used by the
Roman emperor
Constantine I
. Since the vexillum consisted of a flag suspended from
the crossbar of a cross, it was ideally suited to symbolize
crucifixion
. The Chi-Rho symbol was also used by Greek scribes to
mark, in the margin, a particularly valuable or relevant passage; the
combined letters Chi and Rho standing for chrēston, meaning
"good."
Comnenus , or
Manuel
I Komnenos (Greek:
Μανουήλ Α' Κομνηνός, Manouēl I
Komnēnos,
November
28
, 1118
–
September 24
,
1180) was a
Byzantine Emperor
 of the 12th century who reigned over a crucial turning
point in the history of
Byzantium
and the
Mediterranean
. Eager to restore his
empire
to its past glories as the superpower of the Mediterranean world,
Manuel pursued an energetic and ambitious foreign policy. In the process he made
alliances with the Pope
and the resurgent west, invaded
Italy
, successfully handled the passage of the dangerous
Second Crusade
through his empire, and established a Byzantine protectorate
over the
Crusader kingdoms
of
Outremer
.
Facing Muslim
advances in the
Holy Land
,
he made common cause with the
Kingdom of Jerusalem
and participated in a combined invasion of
Fatimid
Egypt
.
Manuel reshaped the political maps of the
Balkans
and
the east Mediterranean, placing the kingdoms of
Hungary
and Outremer under Byzantine
hegemony
and campaigning aggressively against his neighbours both in the west and in the
east. However, towards the end of his reign Manuel's achievements in the east
were compromised by a serious defeat at
Myriokephalon
, which in large part resulted from his arrogance in attacking
a well-defended
Seljuk
position. of the 12th century who reigned over a crucial turning
point in the history of
Byzantium
and the
Mediterranean
. Eager to restore his
empire
to its past glories as the superpower of the Mediterranean world,
Manuel pursued an energetic and ambitious foreign policy. In the process he made
alliances with the Pope
and the resurgent west, invaded
Italy
, successfully handled the passage of the dangerous
Second Crusade
through his empire, and established a Byzantine protectorate
over the
Crusader kingdoms
of
Outremer
.
Facing Muslim
advances in the
Holy Land
,
he made common cause with the
Kingdom of Jerusalem
and participated in a combined invasion of
Fatimid
Egypt
.
Manuel reshaped the political maps of the
Balkans
and
the east Mediterranean, placing the kingdoms of
Hungary
and Outremer under Byzantine
hegemony
and campaigning aggressively against his neighbours both in the west and in the
east. However, towards the end of his reign Manuel's achievements in the east
were compromised by a serious defeat at
Myriokephalon
, which in large part resulted from his arrogance in attacking
a well-defended
Seljuk
position.
Called ho Megas (Greek:
ὁ Μέγας, translated as "the
Great") by the Greeks
, Manuel is known to have inspired intense loyalty in those who served
him. He also appears as the hero of a history written by his secretary,
John
Kinnamos
, in which every virtue is attributed to him. Manuel, who was
influenced by his contact with western Crusaders, enjoyed the reputation of "the
most blessed emperor of
Constantinople
" in parts of the
Latin
world as
well.[1]
Modern historians, however, have been less enthusiastic about him. Some of them
assert that the great power he wielded was not his own personal achievement, but
that of the
dynasty
he represented; they also argue that, since Byzantine imperial power
declined so rapidly after Manuel's death, it is only natural to look for the
causes of this decline in his reign.
|









 of the 12th century who reigned over a crucial turning
point in the history of
Byzantium
and the
Mediterranean
. Eager to restore his
empire
to its past glories as the superpower of the Mediterranean world,
Manuel pursued an energetic and ambitious foreign policy. In the process he made
alliances with the Pope
and the resurgent west, invaded
Italy
, successfully handled the passage of the dangerous
Second Crusade
through his empire, and established a Byzantine protectorate
over the
Crusader kingdoms
of
Outremer
.
Facing Muslim
advances in the
Holy Land
,
he made common cause with the
Kingdom of Jerusalem
and participated in a combined invasion of
Fatimid
Egypt
.
Manuel reshaped the political maps of the
Balkans
and
the east Mediterranean, placing the kingdoms of
Hungary
and Outremer under Byzantine
hegemony
and campaigning aggressively against his neighbours both in the west and in the
east. However, towards the end of his reign Manuel's achievements in the east
were compromised by a serious defeat at
Myriokephalon
, which in large part resulted from his arrogance in attacking
a well-defended
Seljuk
position.
of the 12th century who reigned over a crucial turning
point in the history of
Byzantium
and the
Mediterranean
. Eager to restore his
empire
to its past glories as the superpower of the Mediterranean world,
Manuel pursued an energetic and ambitious foreign policy. In the process he made
alliances with the Pope
and the resurgent west, invaded
Italy
, successfully handled the passage of the dangerous
Second Crusade
through his empire, and established a Byzantine protectorate
over the
Crusader kingdoms
of
Outremer
.
Facing Muslim
advances in the
Holy Land
,
he made common cause with the
Kingdom of Jerusalem
and participated in a combined invasion of
Fatimid
Egypt
.
Manuel reshaped the political maps of the
Balkans
and
the east Mediterranean, placing the kingdoms of
Hungary
and Outremer under Byzantine
hegemony
and campaigning aggressively against his neighbours both in the west and in the
east. However, towards the end of his reign Manuel's achievements in the east
were compromised by a serious defeat at
Myriokephalon
, which in large part resulted from his arrogance in attacking
a well-defended
Seljuk
position.