HAYNES NORTH AMERICAN F-86 SABRE OWNER'S WORKSHOP MANUAL § DAY FIGHTER
VARIANTS 1947 ON
HARDBOUND BOOK
(160 PAGES)
AN INSIGHT INTO
OWNING, FLYING AND MAINTAINING THE USAF's LEGENDARY COLD WAR JET FIGHTER
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
The North
American F-86 Sabre, sometimes called the Sabrejet, was a transonic jet fighter aircraft. Produced by North
American Aviation, the Sabre is best known as the United States' first swept
wing fighter which could counter the similarly-winged Soviet MiG-15 in
high-speed dogfights over the skies of the Korean War (1950§1953). Considered
one of the best and most important fighter aircraft in that war, the F-86 is
also rated highly in comparison with fighters of other eras. Although it was
developed in the late 1940s and was outdated by the end of the '50s, the Sabre
proved versatile and adaptable, and continued as a front-line fighter in
numerous air forces until the last active operational examples were retired by
the Bolivian Air Force in 1994.
Its success led to an extended production run of more
than 7,800 aircraft between 1949 and 1956, in the U.S., Japan and Italy.
Variants were built in Canada and Australia. The Canadair Sabre added another
1,815 airframes, and the significantly redesigned CAC Sabre (sometimes known as
the Avon Sabre or CAC CA-27), had a production run of 112. The Sabre was by far
the most-produced Western jet fighter, with total production of all variants at
9,860 units.
North American Aviation had produced the
propeller-powered P-51 Mustang in World War II, which saw combat against some
of the first operational jet fighters. By late 1944, North American proposed
its first jet fighter to the U.S. Navy which became the FJ-1 Fury. It was an
unexceptional transitional jet fighter which had a straight wing derived from
the P-51. Initial proposals to meet a United States Army Air Forces (USAAF)
requirement for a medium-range, single-seat, high-altitude jet-powered day
escort fighter/fighter bomber were drafted in mid-1944. In early 1945, North
American Aviation submitted four designs. The USAAF selected one design over
the others, and granted North American a contract to build three examples of
the XP-86 (eXperimental Pursuit). Deleting specific
requirements from the FJ-1 Fury, coupled with other modifications, allowed the
XP-86 to be lighter and considerably faster than the Fury, with an estimated
top speed of 582 mph (937 km/h), versus the Fury's 547 mph
(880 km/h). Despite the gain in speed, early studies revealed the XP-86
would have the same performance as its rivals, the XP-80 and XP-84. It was also
feared that, because these designs were more advanced in their development
stages, the XP-86 would be canceled.
Crucially, the XP-86 would not be able to meet the
required top speed of 600 mph (970 km/h); North American had to
quickly come up with a radical change that could leapfrog it over its rivals.
The North American F-86 Sabre was the first American aircraft to take advantage
of flight research data seized from the German aerodynamicists at the end of World
War II. This data showed that a thin swept wing could greatly reduce drag and
delay compressibility problems which had bedeviled even prop-powered fighters
such as the Lockheed P-38 Lightning approaching the speed of sound. By 1944,
German engineers and designers had established the benefits of swept wings
based on experimental designs dating back to 1940. Study of the data showed
that a swept wing would solve their speed problem, while a slat on the wing's
leading edge which extended at low speeds would enhance low-speed stability.
Because development of the XP-86 had reached an advanced
stage, the idea of changing the sweep of the wing was met with resistance from
some senior North American staff. Despite stiff opposition, after good results
were obtained in wind tunnel tests, the swept-wing concept was eventually
adopted. Performance requirements were met by incorporating a 35° swept-back
wing, using NACA 4-digit modified airfoils, using NACA 0009.5§64 at the root
and NACA 0008.5§64 at the tip, with an automatic slat design based on that of
the Messerschmitt Me 262 and an electrically adjustable stabilizer, another
feature of the Me 262A. Many Sabres had the "6§3 wing" (a
fixed-leading edge with 6 inches extended chord at the root and 3 inches
extended chord at the tip) retrofitted after combat experience was gained in
Korea. This modification changed the wing airfoils to the NACA 0009-64 mod at
the root and the NACA 0008.1§64 mod at the tip.
Delays caused by the major redesign meant that
manufacturing did not begin until after World War II. The XP-86 prototype,
which would lead to the F-86 Sabre, was rolled out on 8 August 1947. The maiden
flight occurred on 1 October 1947 with George Welch at the controls, flying
from Muroc Dry Lake (now Edwards AFB), California.
The United States Air Force's Strategic Air Command had
F-86 Sabres in service from 1949 through 1950. The F-86s were assigned to the
22nd Bomb Wing, the 1st Fighter Wing and the 1st Fighter Interceptor Wing. The
F-86 was the primary U.S. air combat fighter during the Korean War, with
significant numbers of the first three production models seeing combat.
The F-86 was produced as both a fighter-interceptor and
fighter-bomber. Several variants were introduced over its production life, with
improvements and different armament implemented (see below). The XP-86 was
fitted with a General Electric J35-C-3 jet engine that produced 4,000 lbf
(18 kN) of thrust. This engine was built by GM's Chevrolet division until
production was turned over to Allison. The General Electric J47-GE-7 engine was
used in the F-86A-1 producing a thrust of 5,200 lbf (23 kN) while the
General Electric J73-GE-3 engine of the F-86H produced 9,250 lbf
(41 kN) of thrust.
The fighter-bomber version (F-86H) could carry up to
2,000 lb (907 kg) of bombs, including an external fuel-type tank that
could carry napalm. Unguided 2.75 in (70 mm) rockets were used on
some fighters on training missions, but 5 inch (127 mm) rockets were
later carried on combat operations. The F-86 could also be fitted with a pair
of external jettisonable jet fuel tanks (four on the F-86F beginning in 1953)
that extended the range of the aircraft. Both the interceptor and
fighter-bomber versions carried six 0.50 in (12.7 mm) M3 Browning
machine guns with electrically boosted feed in the nose (later versions of the
F-86H carried four 20 mm (0.79 in) cannons instead of machine guns).
Firing at a rate of 1,200 rounds per minute, the .50 in (12.7 mm)
guns were harmonized to converge at 1,000 ft (300 m) in front of the aircraft,
using armor-piercing (AP) and armor-piercing incendiary (API) rounds, with one
armor-piercing incendiary tracer (APIT) for every five AP or API rounds. The
API rounds used during the Korean War contained magnesium, which were designed
to ignite upon impact but burned poorly above 35,000 ft (11,000 m) as
oxygen levels were insufficient to sustain combustion at that height. Initial
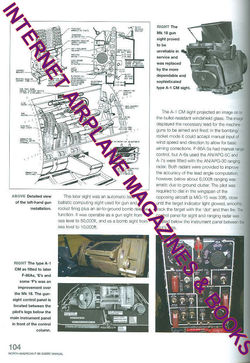
planes were fitted with the Mark 18 manual-ranging computing gun sight. The
last 24 F-86A-5-Nas and F-86E were equipped with the A-1CM gunsight-AN/APG-30
radar which used radar to automatically compute a target's range, which later
proved to be advantageous against MiG opponents over Korea.
The F-86 entered service with the United States Air Force
in 1949, joining the 1st Fighter Wing's 94th Fighter Squadron and became the
primary air-to-air jet fighter used by the Americans in the Korean War. While
earlier straight-winged jets such as the F-80 and F-84 initially achieved air
victories, when the swept wing Soviet MiG-15 was introduced in November 1950,
it outperformed all UN-based aircraft. In response, three squadrons of F-86s
were rushed to the Far East in December. Early variants of the F-86 could not
outturn, but they could outdive the MiG-15, although the MiG-15 was superior to
the early F-86 models in ceiling, acceleration, rate of climb and zoom. With
the introduction of the F-86F in 1953, the two aircraft were more closely
matched, with many combat-experienced pilots claiming a marginal superiority
for the F-86F. MiGs flown from bases in Manchuria by Chinese, North Korean, and
Soviet VVS pilots were pitted against two squadrons of the 4th
Fighter-Interceptor Wing forward-based at K-14, Kimpo, Korea.
Many of the American pilots were experienced World War II
veterans, while the North Koreans and the Chinese lacked combat experience,
thus accounting for much of the F-86's success. However, United Nations pilots
suspected many of the MiG-15s were being flown by experienced Soviet pilots who
also had combat experience in World War II. Former Communist sources now
acknowledge Soviet pilots initially flew the majority of MiG-15s that fought in
Korea, and dispute that more MiG-15s than F-86s were shot down in air combat.
Later in the war, North Korean and Chinese pilots increased their participation
as combat flyers. The North Koreans and their allies periodically contested air
superiority in MiG Alley, an area near the mouth of the Yalu River (the
boundary between Korea and China) over which the most intense air-to-air combat
took place. The F-86E's all-moving tailplane was more effective at speeds near
or exceeding the speed of sound, so the plane could safely recover from a sonic
dive, where the MiG-15 could not safely exceed Mach 0.92, an important
advantage in near-sonic air combat. Far greater emphasis has been given to the
training, aggressiveness and experience of the F-86 pilots. American Sabre
pilots were trained at Nellis, where the casualty rate of their training was so
high they were told, "If you ever see the flag at full staff, take a
picture." Despite rules of engagement to the contrary, F-86 units
frequently initiated combat over MiG bases in the Manchurian
"sanctuary." The hunting of MiGs in Manchuria would lead to many
reels of gun camera footage being 'lost' if the reel revealed the pilot had
violated Chinese airspace.
The needs of combat operation balanced against the need
to maintain an adequate force structure in Western Europe led to the conversion
of the 51st Fighter-Interceptor Wing from the F-80 to the F-86 in December
1951. Two fighter-bomber wings, the 8th and 18th, converted to the F-86F in the
spring of 1953. No. 2 Squadron, South African Air Force also distinguished
itself flying F-86s in Korea as part of the 18 FBW.
In addition to its distinguished service in Korea, USAF
F-86s also served in various stateside and overseas roles throughout the early
part of the Cold War. As newer Century Series fighters came on line, F-86s were
transferred to Air National Guard (ANG) units or the air forces of allied nations.
The last ANG F-86s continued in U.S. service until 1970.
The Republic of China Air Force of Taiwan was an early
recipient of surplus USAF Sabres. From December 1954 to June 1956, the ROC Air
Force received 160 ex-USAF F-86F-1-NA through F-86F-30-NA fighters. By June
1958, the Nationalist Chinese had built up an impressive fighter force, with
320 F-86Fs and seven RF-86Fs having been delivered.
Sabres and MiGs were shortly to battle each other in the
skies of Asia once again in the Second Taiwan Strait Crisis. In August 1958,
the Chinese Communists of the People's Republic of China attempted to force the
Nationalists off of the islands of Quemoy and Matsu by shelling and blockade.
Nationalist F-86Fs flying CAP over the islands found themselves confronted by
Communist MiG-15s and MiG-17s, and there were numerous dogfights.
During these battles, the Nationalist Sabres introduced a
new element into aerial warfare. Under a secret effort designated Operation
Black Magic, the U.S. Navy had provided the ROC with the AIM-9 Sidewinder, its
first infrared-homing air-to-air missile, which was just entering service with
the United States. A small team from VMF-323, a Marine FJ-4 Fury squadron with
later assistance from China Lake and North American Aviation, initially
modified 20 of the F-86 Sabres to carry a pair of Sidewinders on underwing
launch rails and instructed the ROC pilots in their use flying profiles with
USAF F-100s simulating the MiG-17. The MiGs enjoyed an altitude advantage over
the Sabres, as they had in Korea, and Communist Chinese MiGs routinely cruised
over the Nationalist Sabres, only engaging when they had a favorable position.
The Sidewinder took away that advantage and proved to be devastatingly
effective against the MiGs.
In 1954, Pakistan began receiving the first of a total of
120 F-86F Sabres. Many of these aircraft were the F-86F-35 from USAF stocks,
but some were from the later F-86F-40-NA production block, made specifically
for export. Many of the §35s were brought up to §40 standards before they were
delivered to Pakistan, but a few remained §35s. The F-86 was operated by nine
PAF squadrons at various times: Nos. 5, 11, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19 and 26
Squadrons.
During the 22-day Indo-Pakistani War of 1965 the F-86
became the mainstay of the PAF, though the Sabre was no longer a world-class
fighter (due to availability of Supersonic Jets). However many sources state
the F-86 gave the PAF a technological advantage.
The Canadair Sabres (Mark 6), acquired from ex-Luftwaffe
stocks via Iran, were the mainstay of the PAF's day fighter operations during
the Indo-Pakistani War of 1971, and had the challenge of dealing with the
threat from IAF.
At the beginning of the war, PAF had eight squadrons of
F-86 Sabres. Along with the newer fighter types such as the Mirage III and the
Shenyang F-6, the Sabre were tasked with the majority of operations during the
war. In East Pakistan only one PAF F-86 squadron (14th Squadron) was deployed
to face the numerical superiority of the IAF.
PAF F-86s performed well, with Pakistani claims of
downing 31 Indian aircraft in air-to-air combat. These included 17 Hawker
Hunters, eight Sukhoi Su-7 "Fitters", one MiG 21 and three Gnats
while losing seven F-86s.
Two types based on the U.S. F-86F were built under
licence by the Commonwealth Aircraft Corporation (CAC) in Australia, for the
Royal Australian Air Force as the CA-26 (one prototype) and CA-27 (production
variant). The RAAF operated the CA-27 from 1956 to 1971. Ex-RAAF Avon Sabres
were operated by the Royal Malaysian Air Force (TUDM) between 1969 and 1972. From 1973 to 1975, 23 Avon Sabres
were donated to the Indonesian Air Force (TNI-AU); five of these were ex-Malaysian aircraft.
The CAC Sabres included a 60% fuselage redesign, to
accommodate the Rolls-Royce Avon Mk 26 engine, which had roughly 50% more
thrust than the J47, as well as 30 mm Aden cannons and AIM-9 Sidewinder
missiles. As a consequence of its powerplant, the Australian-built Sabres are
commonly referred to as the Avon Sabre.
CAC manufactured 112 of these aircraft.
XF-86: three prototypes, originally
designated XP-86, North American
model NA-140
YF-86A: this was the first prototype fitted
with a General electric J47 turbojet engine.
F-86A: 554 built, North American model
NA-151 (F-86A-1 block and first order of A-5 block) and NA-161 (second F-86A-5
block)
DF-86A: A few F-86A conversions as drone directors
RF-86A: 11 F-86A conversions with three cameras for reconnaissance
F-86B: 188 ordered as upgraded A-model with wider fuselage and larger tires but
delivered as F-86A-5, North American model NA-152
F-86C: original designation for the YF-93, two built, 48§317 & 48§318,
order for 118 cancelled, North American model NA-157
YF-86D: prototype all-weather interceptor originally ordered as YF-95A, two built but designation
changed to YF-86D, North American model NA-164
F-86D/L: A transonic all-weather search-radar equipped interceptor originally
designated F-95A, 2,506 built. The F-86D had only 25 percent commonality with
other Sabre variants, with a larger fuselage, larger afterburning engine, and a
distinctive nose radome. Sole armament was Mk. 4 unguided rockets instead of
machine guns. F-86Ls were upgraded F-86Ds.
F-86E: Improved flight control system and
an "all-flying tail" (This system changed to a full power-operated
control with an "artificial feel" built into the aircraft's controls
to give the pilot forces on the stick that were still conventional, but light
enough for superior combat control. It improved high-speed maneuverability);
456 built, North American model NA-170 (F-86E-1 and E-5 blocks), NA-172,
essentially the F-86F airframe with the F-86E engine (F-86E-10 and E-15
blocks); 60 of these built by Canadair for USAF (F-86E-6)